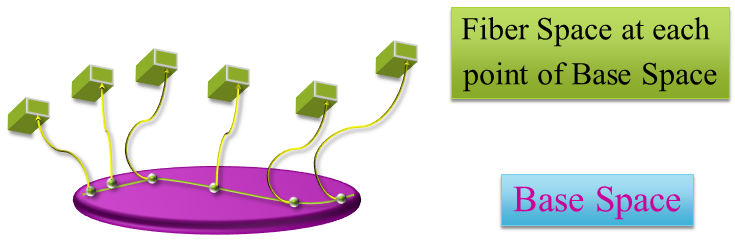
Basically a fiber bundle is a pair of a "base space" - think of it as some geometric
entity - with a "fiber" attached to each point. This "fiber" is any kind of attribute
information per point, such as color, temperature, brightness or anything more.

In the HydroVish fiber bundle data model geometric entities are organized into Grid objects with attribute information living on Fields. A general data set consists of many Grids stored in a Bundle. There is no limit on how many Grids may live on a Bundle, and there is no limit on how many Fields may live on each Grid.
Within a Bundle a Grid is selected via a name that the user is free to specify according to their needs when creating the data set. For instance it is useful to use a name that refers to the origin of the data, such as the name of an project, or some geographical region. In many cases, a Bundle may contain only a single Grid, though the infrastructure supports many, which e.g. allows easy switching and comparisons between projects, regions, etc.
Within a Grid a Field is selected via a name that describes the meaning of this information. While technically arbitrary, various applications introduce certain conventions on how to call which information.
Visualization and data processing modules may operate on either Grid or Field objects, depending on how much information they require. When reading a data file, all data will be provided as a Bundle:
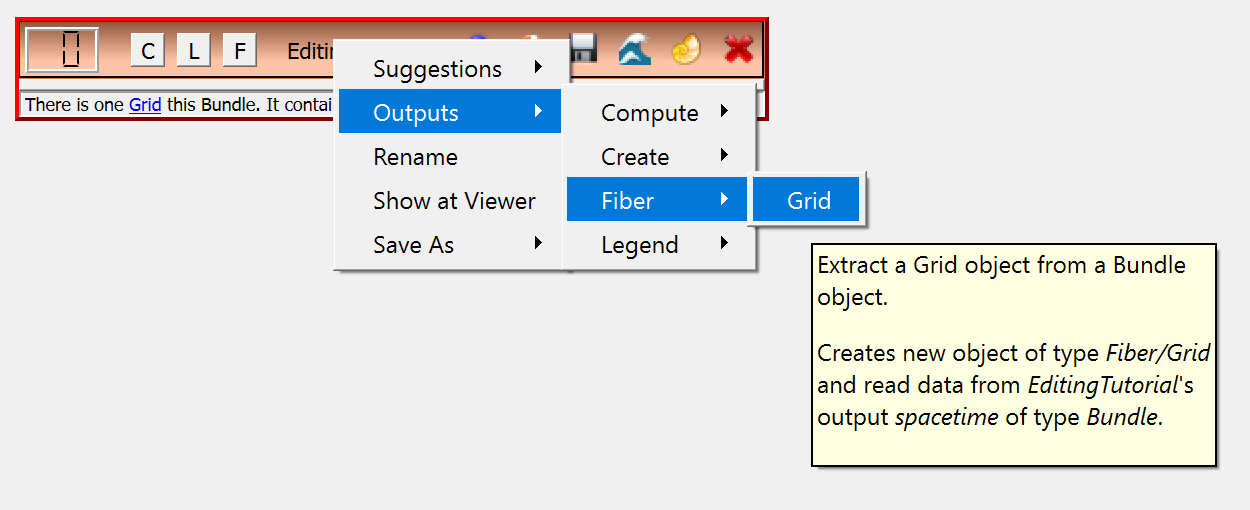
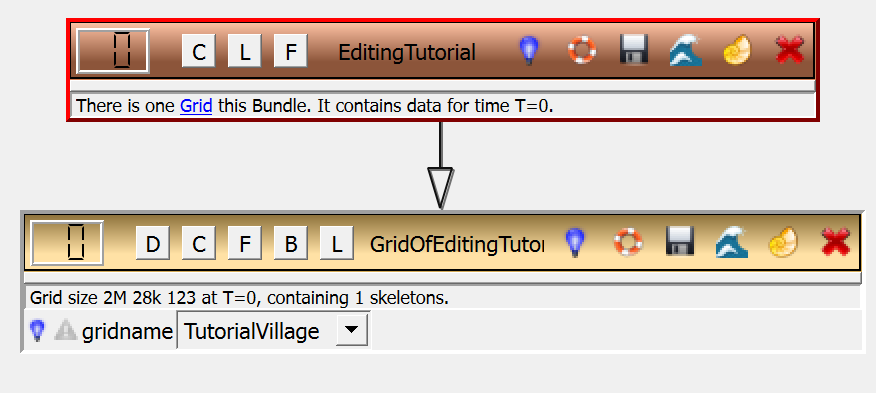
Starting from these initial steps, more advanced visualization networks are ready to be constructed, such as in the Editing Tutorial.
hydrovish.exe EditingTutorial=more.f5 myscript.vis
for a bundle object named "EditingTutorial". The script will work as before.
For an overview of all VISH help topics see the Table of Contents.
